Tense: Types | Formation | Uses { with examples}
Hello scholars, welcome to HSC exam guide. As soon as a student rolls into school the process of 'learning grammar' starts. For a better understanding of any language, it is necessary too. In any language, Tense is the base of its learning. If you understand the concept very well, its formation, its types, which tense is used in certain situations, then you definitely learn that language perfectly. You can even speak that language fluently. So here is the article for you to learn everything about ‘Tense in English’.
What is tense?
In simple words, Tense means time. In a sentence, an action word (verb) is used to express the time of that sentence. It expresses whether the action took place some time ago ( past), whether it is taking place in the current situation (Present) or whether it will happen after some time from now (future). It means, it is the verb that shows the time. How? by using its different forms. And these forms are called Tense. There are 4 forms of the verb.
Base verb:
As the name suggests these verbs are the root action words. It is also known as an infinitive. It is used to show present or future action.
Examples:
make- I will make a nice dish.
give- They give worth advice.
attract- Honey attracts bees. etc.
Simple Past verb:
Examples:
made- I made a nice dish.
gave- They gave worth advice.
attracted- Honey Bees attracted to honey.
Past Participle:
Examples:
made- I have made a nice dish.
given- They will have given worth advice.
attracted- Honey Bees had attracted towards honey. etc.
Present participle:
This verb form indicates the action that is going on. This action can be going on in the past, present, or future.Examples:
speaking- He is speaking very gently.make- I was making a nice dish.
give- They had been given worth advice.
attract- Honey will have been attracting bees. etc.
Now let's understand how these verb forms are used to express the time of action and form different types of tense.
Other Topics
Class 12 English poem Indian weavers
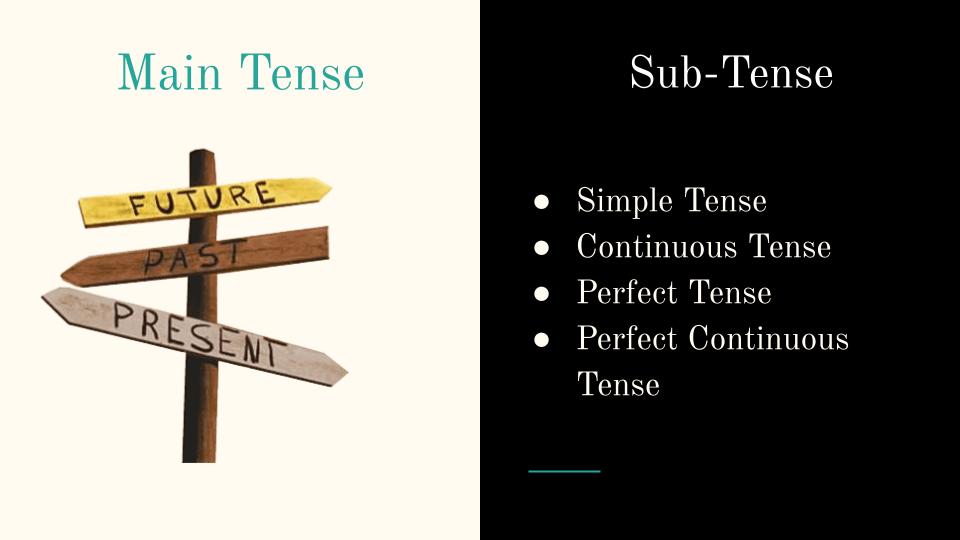
Types of Tense
In the above discussion, you come to know that Past, Present, and Future are three major or main tenses. The verb form discussed earlier makes 4 subtypes of tense.
- Simple Tense
- continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect continuous Tense
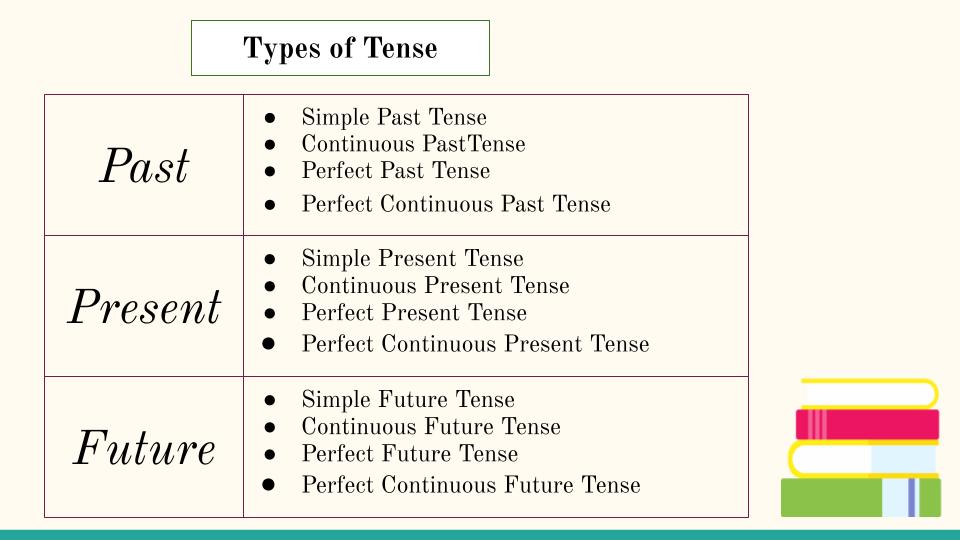
12 types of Tense:
Past Tense:
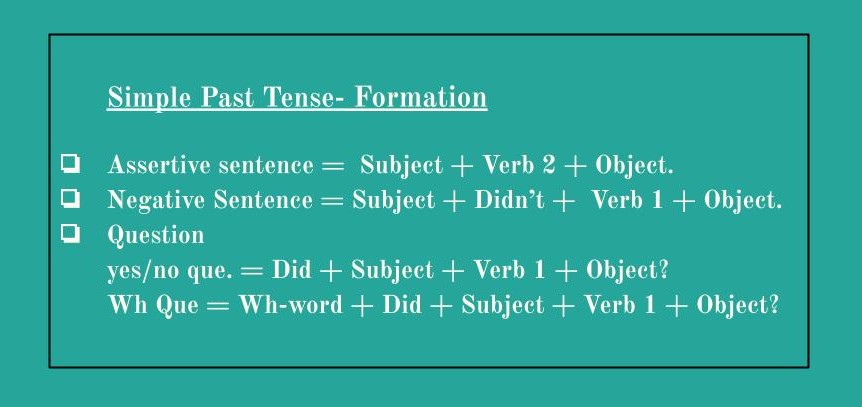
1) Simple Past Tense:
formation/ structure: Subject+ verb 2+ object.
Uses:
- To indicate the actions finished before the time of speaking.
- To indicate some past habits.
- To indicate the recent past.
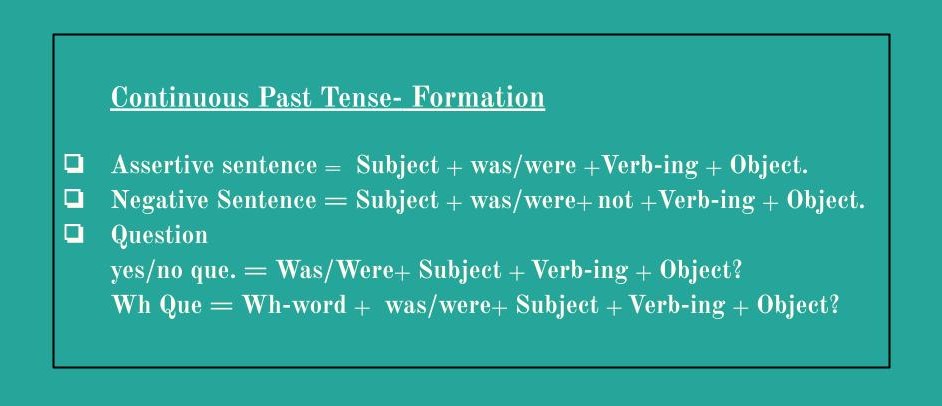
2) Continuous Past Tense:
Formation/ structure: Subject + was/were + verb-ing + object.
Note: Was- for a singular subject. Were- for the plural form of the subject.
(In past continuous tense continuity is denoted by the helping verb was and we're)
Uses:
- To indicate progressive action that took place in the e.g. The father and son were walking through the forest.
- To indicate a continuing action at some point in the past, when another event took place. e.g. Mr. Sharma was waiting for a bus when I reached there.
- To describe two or more actions going on at the same time in the past. e.g. Reena was studying hard while others were wasting their time scrolling the mobile.
Examples:
- Jo was always scandalizing Meg by her queer performance.
- She was standing before a fine portrait of the old gentleman when the door opened again.
- Hillary and I were moving about twenty feet apart.
- They were lying flat against the summit.
- A visit to the agricultural officer was enlightening.
- It was a bewildering crisscross of light rays and moving shadows.
- Mrs.Holman was leaning forward and telling her about her son.
- It was the beginning of a new journey for him.
- I was sitting at my mess table in the hostel.
- His wife was waiting for him at the door.
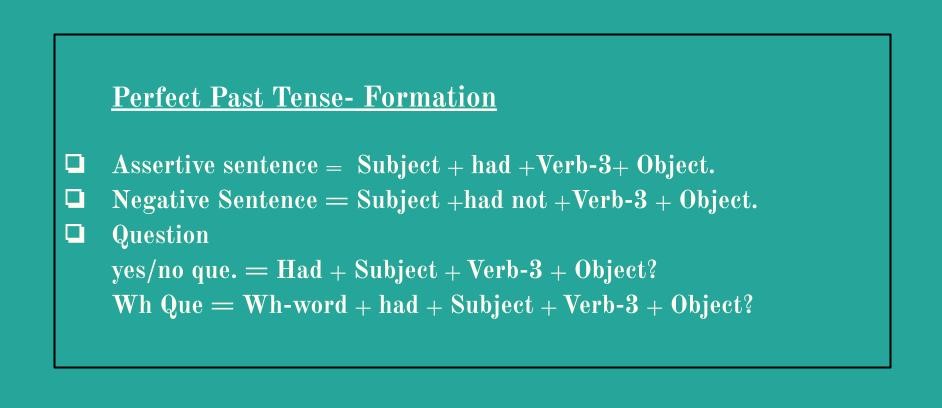
Formation/ structure: Subject + had + verb 3 + object.
Uses:
- To indicate an action took place before the past. It is the past of the past. e.g. The train had left when I reached the station.
- To indicate the past action which denotes causes or reasons for later action in the past. e.g. He did not attend the meeting because he had missed his train.
- To express an unfulfilled wish in the past. e.g. I wish I had met him once.
- To express an unfulfilled condition in the past. e.g. If he had worked hard, he would have got a promotion.
Examples:
- I had left home without any money.
- I had learnt from my childhood that money does not mean everything in life.
- You have secured the first rank in the university.
- I had developed an inferiority complex.
- He had left his village without any previous thought or plan.
- The jungle had taken a toll on him.
- I had forgotten about them in the excitement of the theft.
- Jo had planned many ways of making friends with him.
- He had not in the least intended to be an astrologer.
- Long practice had sharpened his perception.
4) Perfect Continuous Past Tense
Uses:
To express an action that had begun and continued for a certain time in the past. e.g. I had been living there for ten years.
Examples:
- They had been learning through each subject.
- Gas burner, which had been burning for eighty days.
- He had been poaching on the nearby estate,
- You had been singing.
- I had been working for Anil for almost a month
- She had been saving every penny
- He had been squatting on the pavement for years,
- Everyone had been calling her Bholi the simpleton.
- They had been going
- They had been working on it since last year.
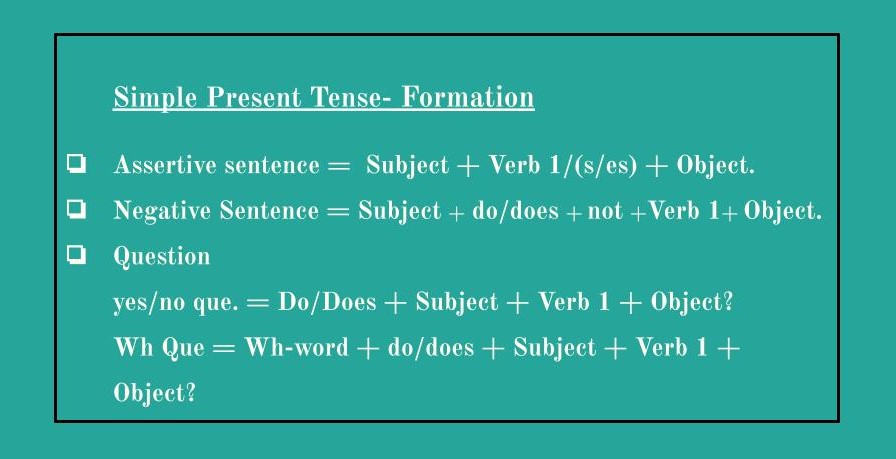
Present Tense:
Formation/ structure: Subject + verb 1 ( s/es for singular subject) + object.
e.g. He/she goes.
I/we/you/they go.
Uses:
- To Indicate habitual action. e.g. He practices yoga every day.
- To express permanent truth or fact. e.g.The Earth moves around the Sun.
- To indicate routine matter. e. g. he plays football.
Examples:
- We travel to open our hearts and eyes.
- Travel guides us toward a better balance of wisdom and compassion.
- The sovereign freedom of traveling comes from the fact that it whirls you around.
- We carry values and beliefs.
- I go to Iceland to visit the lunar spaces within me.
- The placement offer maps of the great temples of the city.
- This creates resentment among locals towards the animals.
- Data helps in monitoring the outbreaks of epidemics and diseases.
- Your GPS and Google Maps make use of Big Data.
- Weather patterns give us warnings of impending natural calamities.
2) Continuous Present Tense
Is - for singular subject
Are - for plural form of subject
e.g. I am ___
He/she is____.
we/you/they are_____.
Uses:
- To indicate the action that takes place at the time of speaking. e.g. Are you going?
- To indicate the action that is in progress and will be continued. e.g. Anny is working on science fiction.
- To indicate the action that is arranged to take place in the near future. e.g. I am going to explain the conversion of tense in my next post.
Examples
- Why am I telling you my story?
- You are traveling through several cultures in as many minutes.
- I am treading cautiously among the woods.
- The network of alarm calls is expanding its range.
- The animals are paying me back.
- That boy is suffering for society and fun.
- we are cherishing a great delusion
- You understand what I am talking about?
- He is expressing his wonder at the ways of Nature
- We are living over a plague-spot.
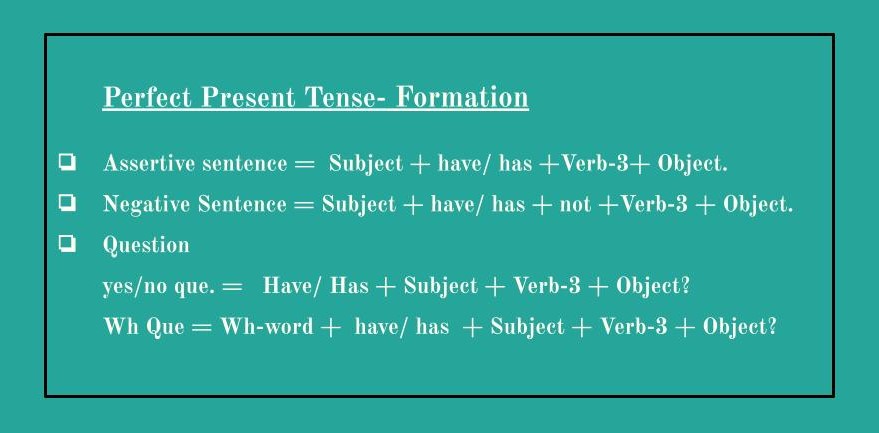
Formation/ structure: Subject + have/ has + verb 3 + object.
Has- for a singular verb.
e.g. He/she has_.
I/we/you/they have__.
Uses:
- To indicate just completed actions e.g. He has just left for the office.
- To express the action that took place in the past but is connected with the present. e.g. I have seen the movie.
Examples
- Shaaz has managed to collect precious footage.
- The forests have taught me many things.
- The black panther has taught me patience.
- If you have ordered something online you can trace the location of your goods.
- New insights have enabled the banks and finance companies to come with suitable plans.
- I have written about 34 books in Marathi.
- My book boardroom on management has created at least 20 successful entrepreneurs.
- Dr. B. R. Ambedkar has expressed his deep concern over the absence of two things in the then Indian society.
- Although Sadie has passed her test, she never drives.
- He has escaped my hands.
Formation/ structure: Subject + have/has+been+ verb-ing+ object.
Uses:
- To indicate an action that began in the past and is still continuing. e.g. He has been living here for two years.
Examples:
- GPS has been identifying the exact location of the place.
- The child has been asking for sweets for so many days now.
- Dr. Sengupta has been trying to master the craft for the last five years.
- My wife has been having a severe headache since yesterday.
- Your mother has been chatting for very long on the telephone.
- You have been waiting long at the city bus-stop
- She has been writing since childhood.
- Children have been crafting for two hours.
- The farmer has been digging for a long time.
- We have been traveling since last night.
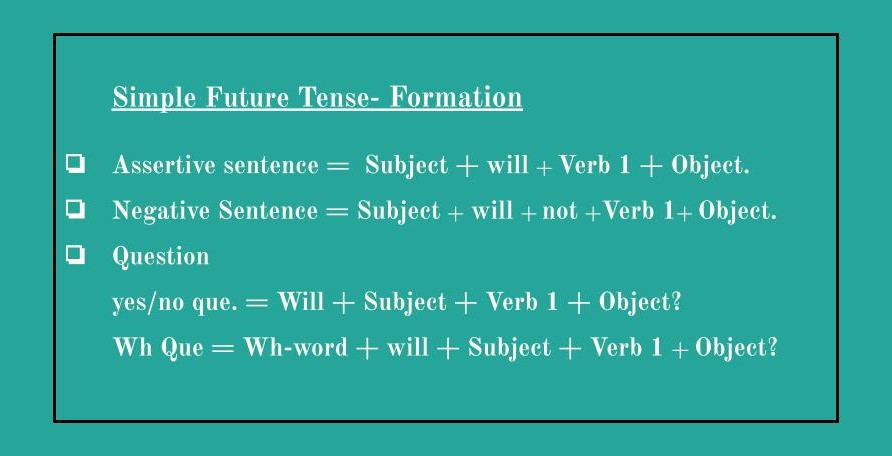
Future Tense:
Formation/ structure: Subject + will +verb 1 + object
Uses:
- To express an action that is almost certain to happen in the near future.
Examples
- I will speak to you tomorrow.
- You will find Teriyaki MacBurgers and Bacon Potato Pies.
- Will you come, please?
- we will not take part in any controversy.
- ‘Mahalaxmi, the local Goddess, will give you the seeds of Kasbai.’
- ‘Will you carry him in there first?’
- I will prepare some nice stuff for her.
- it will permit me to retaliate with reasonable violence.
- This will allow better revenue from ads
- I will take this route.
Formation/ structure: Subject + Will be + Verb -ing + object.
Uses:
- To express an action that is expected to take place and be progressive in the future.
Examples
- In Politics, we will be recognizing the principle of ‘one man one vote’ and ‘one vote one value’.
- You will be arresting today or tomorrow,
- The answers will be astounding.
- My sister will be taking her IPS exam next month.
- Will you be having a cup of tea with Mr. Phillips?
- A fresh stock of clothes will be arriving next week.
- They will be managing the event.
- I will be warning them about it.
- The Currency will be going down next week.
- Lots of opportunities will be waiting for you.
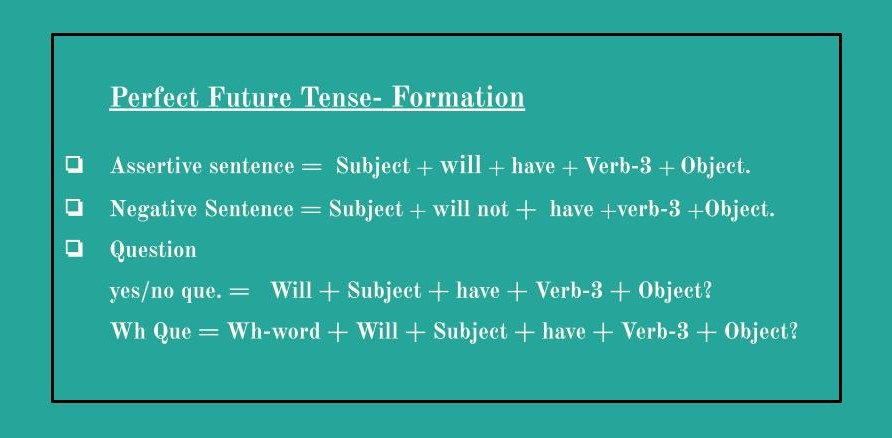
3) Perfect Future Tense
Uses:
- To express an action completed before a given movement in the future. e.g. She will have gone before we reach there.
Examples
- By next May, He will have written his second novel
- You will have passed out before Jerry joins the school.
- He will have heard the story by then.
- Rama will have reached there before the train arrives.
- Before you go to see him, he will have left the place.
Formation/ structure: Subject + Will have been + Verb -ing + object.
Uses:
- To express an action that is in progress over some time that will end in the future.
Examples:
- They will have been waiting there for the whole day.
- I will have been teaching here for twenty years.
- He will have been working in this office for six years.
- She will have been preparing for the SSC competitive exam for the last three years.
Other Topics

















2 Comments
This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteBro Daily Use English Words Par Likho Kuch
ReplyDelete